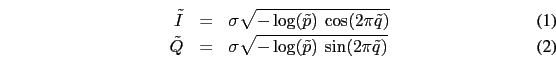Gaussian White Noise Generator block
In communication system simulator, a Gaussian noise generator is generally computed using the box Muller law.
This method allows noising both amplitude and phase a given complex value.
It is defined with these two equations:
where 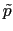 and
and 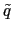 are two uniform random variables,
are two uniform random variables, 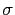 the variance of the noise source and
the variance of the noise source and 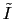
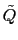 the real and imaginary part of the noisy complex sample.
the real and imaginary part of the noisy complex sample.
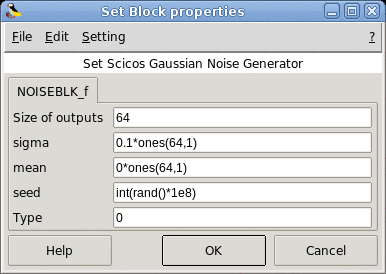
- Size of outputs
The size of the regular output port
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1. Integer.
- sigma
The variance of the noise generator.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size -1. Vector of real
- mean
The mean of the noise generator.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size -1. Vector of real.
- seed
The seed of the noise generator.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1. Scalar.
- Type
The type of the noise generator.
Properties : Type 'vec' of size 1. Integer.
- 0
for a cosine output
- 1
for a sine output
- 2
for both cosine and sine output (two regular outputs)
- always active: no
- direct-feedthrough: no
- zero-crossing: no
- mode: no
- regular outputs:
- port 1 : size [64,1] / type 1
- number/sizes of activation inputs: 1
- number/sizes of activation outputs: 0
- continuous-time state: no
- discrete-time state: no
- object discrete-time state: no
- name of computational function: noiseblk
- MODNUMCOS/macros/scicos_blocks/Sources/NOISEBLK_f.sci [view code]
- MODNUMCOS/routines/sources/noiseblk.c (Type 4) [view code]
A. Layec